News
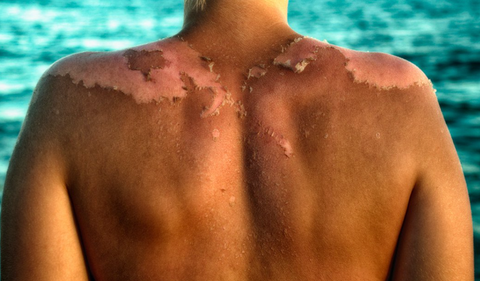
Skin cancer remains a significant global health challenge, particularly in regions with high ultraviolet (UV) exposure. While traditional methods of protection, such as sunscreen, have proven effective, recent research has focused on supplements that may enhance skin defenses from within. Among these, nicotinamide (a form of vitamin B3) has shown promising results in reducing skin cancer incidence. This article delves into the 2015 study published in The New England Journal of Medicine that highlighted nicotinamide’s efficacy in skin cancer prevention and discusses its role as a novel supplement in enhancing skin resilience against UV radiation.

Sun supplements are designed to protect skin from UV damage and other environmental stressors using key ingredients like nicotinamide (Vitamin B3) and Polypodium Leucotomos.
Nicotinamide: Enhances DNA repair, boosts the skin’s immune response, and reduces the risk of non-melanoma skin cancers.
Polypodium Leucotomos: Provides potent antioxidant properties, reduces oxidative stress, and helps maintain skin’s structural integrity.
